Introduction
Product Development Life Cycle: In the fast-paced world of business and innovation, bringing a successful product to market involves a strategic journey known as the Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC). This well-defined process guides companies through the stages of conceptualization, design, development, testing, and launch. In this blog, we’ll delve into the various phases of the PDLC, elucidating each step with real-world examples that showcase the importance of a systematic approach to product development.
Table of Contents
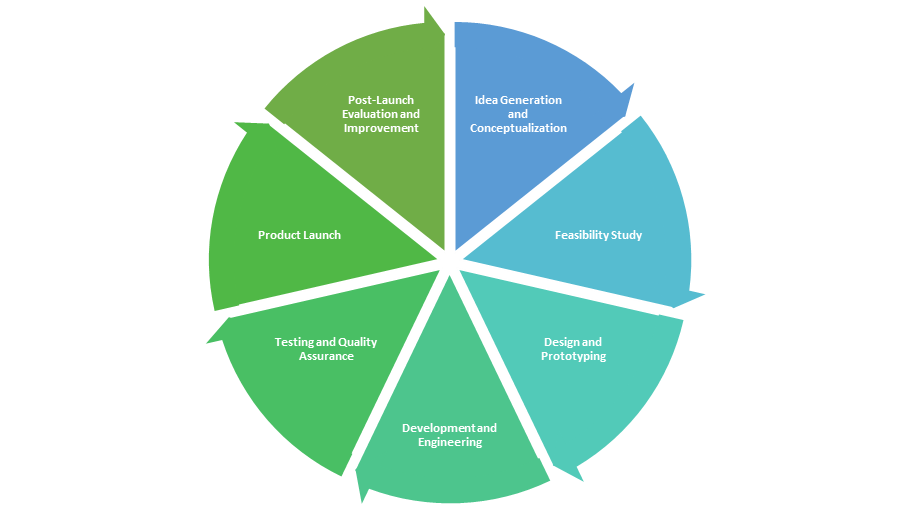
Stages of the Product Development Life Cycle

Product Development Life Cycle
1. Idea Generation and Conceptualization
The journey begins with the birth of an idea – a solution to a customer problem or an opportunity in the market. This phase involves brainstorming, market research, and validation to ensure that the idea aligns with the company’s vision and customer needs.
Example: Consider Apple’s iPod. The idea emerged from the desire to create a portable music player that could store thousands of songs, providing a sleek alternative to bulky CD players.
2. Feasibility Study
In this stage, companies assess the technical, financial, and operational feasibility of the idea. They analyze potential risks, resource requirements, and potential market demand to determine if the idea is worth pursuing.
Example: Before launching the Tesla Model 3, Tesla conducted a feasibility study to ensure that the electric car’s production could be scaled to meet high demand and that it was financially viable.
3. Design and Prototyping
This phase involves translating the idea into a concrete design. Prototypes and mock-ups are created to visualize the product’s appearance and functionality. Iterative design processes refine the product’s features based on feedback and testing.
Example: The development of the iPhone involved numerous design iterations to achieve the right balance of sleek aesthetics, user-friendly interface, and advanced technology.
4. Development and Engineering
In this stage, the product is built based on the approved design. Engineers and developers work to code, manufacture, and assemble the components of the product. Quality assurance checks ensure that the product meets predetermined specifications.
Example: Microsoft’s Windows operating system goes through intensive development and engineering to ensure compatibility, security, and a smooth user experience across different devices.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Before a product reaches the market, it undergoes rigorous testing to identify and rectify defects, bugs, and usability issues. Quality assurance teams work to ensure the product meets the desired standards.
Example: Video game companies like Ubisoft extensively test their games to identify and fix glitches, improve gameplay mechanics, and optimize performance before release.
6. Product Launch
The highly anticipated launch marks the introduction of the product to the market. Marketing campaigns, promotional activities, and distribution strategies are executed to generate awareness and drive sales.
Example: The launch of the Apple Watch involved an elaborate unveiling event, generating buzz and creating a sense of exclusivity around the product.
7. Post-Launch Evaluation and Improvement
After the product is in the hands of consumers, companies gather feedback and monitor performance. Continuous improvements and updates are made based on user reviews, usage patterns, and market trends.
Example: Social media platforms like Facebook constantly roll out updates to enhance user experience, add new features, and address privacy concerns.
Product Development Life Cycle : Conclusion
The Product Development Life Cycle is a structured framework that guides companies from ideation to the successful launch of a product. Each phase serves a crucial purpose, from idea generation and feasibility assessment to design, development, testing, and post-launch improvements. Real-world examples showcase the significance of a well-executed PDLC in creating products that resonate with customers, meet market demands, and achieve long-term success. As technology and consumer preferences evolve, mastering the art of product development has never been more vital for companies striving to stay competitive and innovative.
Scrum Guide for Roles in Agile Way of Working for Product Owner

